There are many reasons why you might want to search for a registered copyright, including to verify that a work was registered properly or to determine who to contact about licensing a work.
I conducted my first search when a romance writer friend asked me to help her verify that the copyright in her books were registered properly. It may seem daunting to search for a copyright, but you’ll see it’s a straightforward process through the U.S. Copyright Office website.
Step One: Copyright.gov
The homepage for the U.S. Copyright Office has a block clearly labeled “Search Copyright Records” to search for records dating in or after 1978.
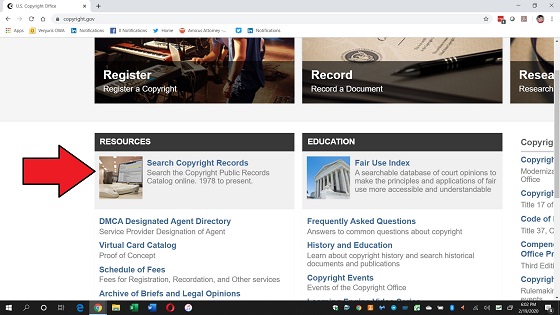
Step Two: Search by Name
This link takes you to a search page where you can search for registered works by title, name, or keyword. Unless you have specific information about the registered copyright you’re looking for, it’s probably best to search by name. You can search by the author’s or copyright owner’s name or their company name.
You can search by title, which is a good option for things books where people tend to know it, but you may not know the title of works like websites or a collection of photographs.
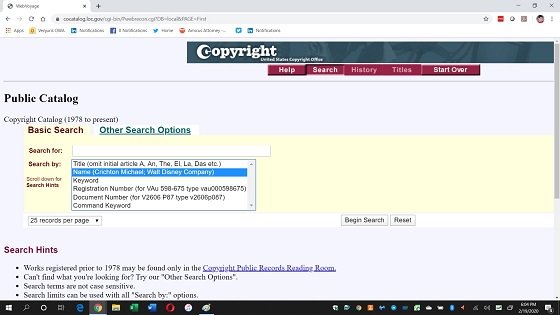
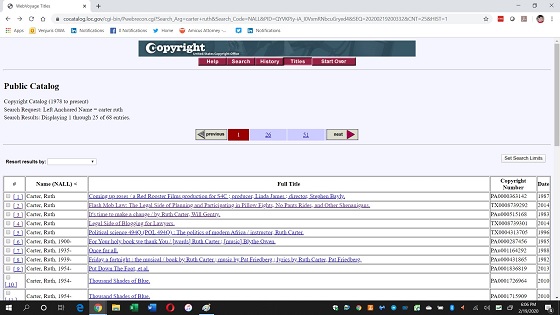
Step Three: Review the Results
Hopefully the search results aren’t too long, and it’s easy to find the work you’re looking for. Each record will include the name of the work, the type of work it is, the author’s name, and information about who to contact about the rights to the work.
Many times, the author for the work is not the owner of the copyright or the person to contact about it.
Benefits of Copyright Registration
There are three main situations where I recommend a client register their copyright:
- They want to license their work.
- They want to sell the copyright in their work.
- They want the option to sue in the event their copyright is infringed.
In the U.S., you cannot sue for copyright infringement unless you’ve previously registered your copyright. When you register you work will impact what types of damages you can request from the court.
If you have questions about your copyright rights, please contact me or another copyright lawyer in your community.